The emergence of the Internet has been one of the most significant events in the history of mankind, which came to revolutionize and transform the way we communicate, learn, work and interact with the world around us.
From its birth in the 1960s as a research project to its current status as a global network, the Internet has evolved in multiple dimensions, and its impact on society is undeniable.
In this article we will explore the beginnings and evolution of the Internet.
Origins of the Internet
The Internet is a global network of interconnected devices that can be accessed from anywhere and has changed the way we live and work.
But where did it all start?
The origins of the Internet date back to the 1960s, when the U.S. Department of Defense initiated a research project called ARPANET.
Their goal was to create a secure, failure-safe communications network capable of surviving a nuclear attack.
As ARPANET expanded, it became an open network that allowed people around the world to connect and communicate.
Web1: the beginnings of the Internet
The Web1, also known as the static Web, was the first stage in the evolution of the World Wide Web.
It was a basic text-only version of the Internet, with static pages that did not change much, where basic information was shared and users could only consume content, not create it.
These early web pages were created using HTML and FTP (File Transfer Protocol) to display text, images and hyperlinks, but lacked features such as embedded videos or design elements that are common today.
This meant that creators had to manually code their sites and update them every time they wanted to add new material.
Web2: the social web
As the Internet evolved, users began to use it to share information and connect with others around the world. This led to the creation of Web2.
Websites ceased to be merely a means of accessing static information and became an interactive space where users actively engage with web content, participate in discussions and express opinions through online platforms such as social networks, forums, blogs, wikis, podcasts or video sharing sites.
As a result, Web2 became more social and collaborative, and companies began to use it as a tool for marketing and communication with their customers.
One of the key features of Web 2 is not only its ability to facilitate social connectivity, but also its personalization aspect.
This allowed websites to tailor content based on individual preferences gathered from user activities or data analysis.
In Web2, users have no control over the data and information that is collected, and it is the large technological companies that store and use it.
And it all boils down to one transaction: you give me your data and I let you use my application.
Web3: the present and future
Web3 is the third and most advanced version of the World Wide Web.
It uses technologies such as semantic web, machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain to provide a smarter, more secure and decentralized network.
It is considered the next generation Internet, where everything that could be done in Web2 can still be done, but in a decentralized way.
Unlike previous versions of the Internet, Web3 is based on decentralized protocols that allow more control over data and protect user privacy.
It also promotes greater transparency and fairness in the digital economy, while addressing issues such as property of data and online security.
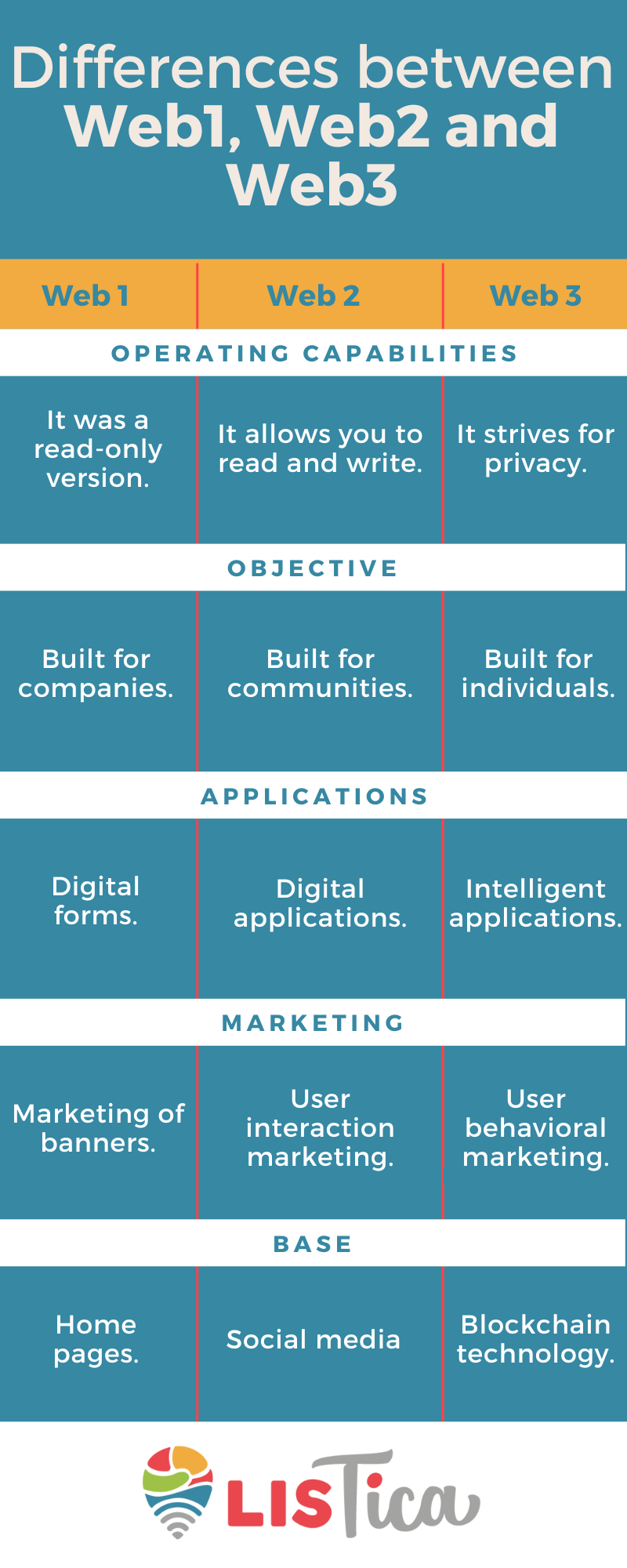
Differences between Web1, Web2 and Web3
The integration of Web1, Web2 and Web3 concepts has the potential to create a more inclusive and accessible web for all users.
Here you can find some of their differences:
In conclusion, the Internet has evolved a lot since its inception and will continue to do so in the future.
Each iteration has enabled greater collaboration and connectivity among users, leading to the creation of new forms of interaction and emerging technologies.
Did you know the differences between Web1, Web2 and Web3?
